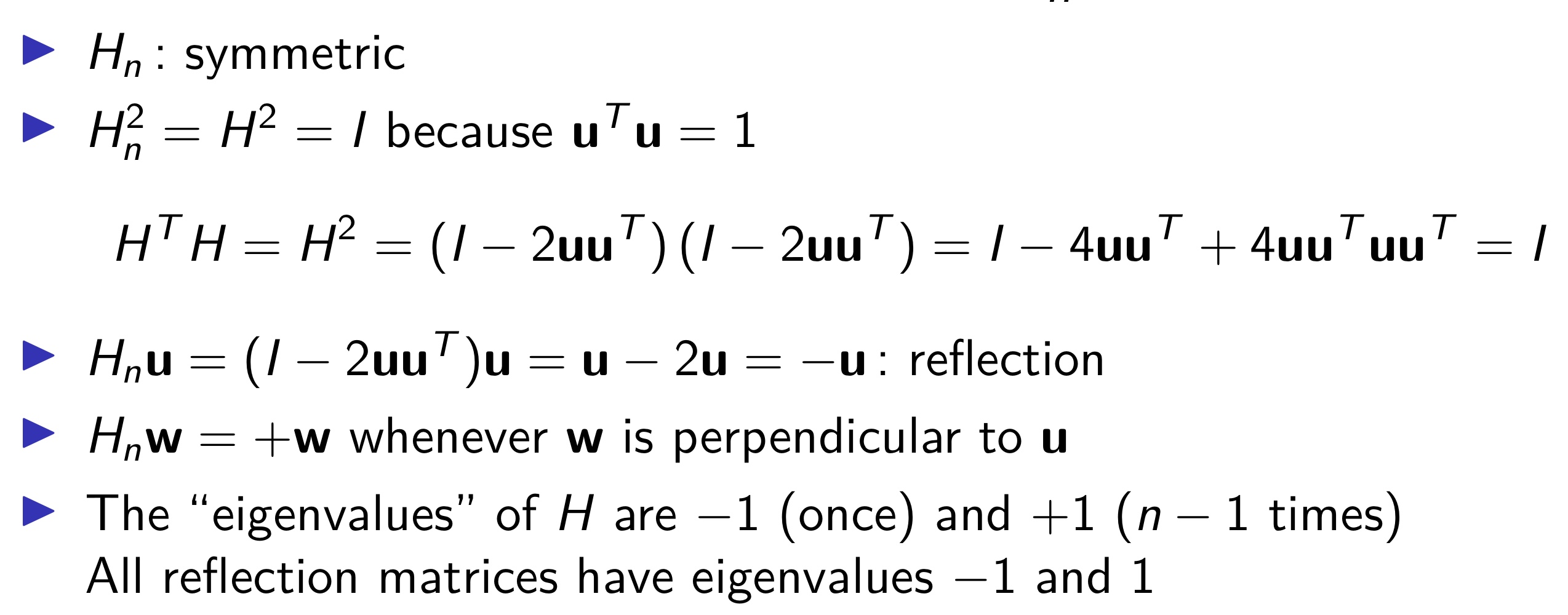Special Matrix
Table of contents
- 0. Symmetric Matrix
- 1. Orthogonal Matrix
- 2. Hadamard Matrix (아다마르 행렬)
- 3. Projection Matrix → Least Square Error
- 4. Rotation and Reflection
- 5. Householder Matrix
0. Symmetric Matrix
- Properties
- $\forall \lambda$ : real
- $\exists \lbrace x_i \rbrace$ : orthonormal and full (spans $V$). ($\implies$ diagonalizable : spectral thm. )
- Spectral Theorem
1. Orthogonal Matrix
: transpose rather than inverse
- Rectangular $Q$ : tall thin matrix with orthonormal columns ($m \times n, m \gt n$)
- Definition (
Orthonomal Matrix)- $Q$ : square matrix with orthonormal columns ($n \times n$)
- iff conditions
- $Q^TQ = QQ^T = I_n$
- Properties
- $Q_1, Q_2 \text{ : orthogonal} \implies Q_1Q_2 \text{ : orthogonal}$
- $ \lVert Q\mathbf{x} \rVert = \lVert \mathbf{x} \rVert $ : isometry
- orthogonal $\implies$ rotation
2. Hadamard Matrix (아다마르 행렬)
- Definition, notation
- $H_n$ : entries are $\pm 1$, and rows/columns are mutually orthogonal.
- Properties
- $H_n$ is not orthogonal. (scalar multipled orthogonal matrix)
- Hadamard Conjecture
- $H_n$ exists iff $n \equiv 0 (\text{mod } 4)$
3. Projection Matrix → Least Square Error
\[P : R^n \xrightarrow{\text{proj}} C(P)\] \[P : \mathbf{b} \mapsto P\mathbf{b}\]- Definition
- $P$ : square matrix $s.t.$ $P^2=P$ : idempotent
- “projection twice = projection once”
- Definition (Orthogonal Projection Matrix)
- $P^2 = P = P^T$ : idempotent and symmetric
4. Rotation and Reflection
\[Q_{\text{rotate}} = \begin{bmatrix} cos\theta & -sin\theta \\ sin\theta & \ \ \ cos\theta \end{bmatrix} \text{ : rotate } \theta \quad\] \[Q_{\text{reflect}} = \begin{bmatrix} cos2\theta & \ \ \ sin2\theta \\ sin2\theta & -cos2\theta \end{bmatrix} \text{ : rotate } \pi + 2\theta\]- rotation $\times$ rotation : rotation
- reflection $\times$ reflection : rotation
- rotation $\times$ reflection : reflection
5. Householder Matrix
\[H_n = I_n - 2\mathbf{u}\mathbf{u^T}\]where $\mathbf{u}$ is a unit vector
- Properties :